How to Set Up CI/CD in a React Project with Circle CI, AWS S3, and AWS CloudFront

Good developers are always looking for ways to reduce repetitive, manual processes. Leveraging CI/CD (Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery) methodologies helps developers automate processes so they can focus valuable time on developing new, innovative, and problem-solving features.
In the present software development context, important workflows for software development are often run, tested, built, and deployed without setting up CI/CD, meaning that all the processes in the software development cycle are done manually, from running tests to running the build, to getting the build file and deploying on the server. These manual processes quickly become inefficient. Setting up CI/CD helps alleviate these burdens by automating much of the software development process, making it easy to test and deploy end products.
Tutorial Overview
In this tutorial, we will be integrating CI/CD into a development cycle by:
- Creating a React application and pushing the repo to GitHub.
- Setting up AWS S3 for deployment.
- Setting AWS Cloudfront with HTTPS and CDN.
- Setting up CircleCI to subscribing repository and trigger it when a commit is received to start the test, build, and deployment to AWS.
Now, the steps that we will take to set this up are:
- When pushing code to the repository (e.g. GitHub, Bitbucket), the repository will send a trigger (webhook) to CI that subscribes to this repository.
- CI server starts the run command that we prepared (e.g. run test, check syntax, build, deploy).
- In case an error occurs, a notification will be sent.
- A developer will fix the bug and commit code again and loop back to first until the error is resolved.
The steps to setup CI/CD to React ecosystem is explained below:
Step 1: Setting up your repository
First, we are going to set up a repository in GitHub. In the GitHub console interface, we just need to click on the Create new repository button and the following screen will appear:

Here, we need to enter the project repository name and mark it as public or private. (Note that making the repository private is not free.)
Now, we need to create a React project and add git configuration to it by running the following commands:
$ npx create-react-app my-react
$ cd my-react
$ git init
$ git add .
$ git commit -m 'initial commit'
$ git remote add origin https://github.com/krissnawat/my-react.git
$ git push -u origin master
Step 2: Setting up AWS S3
Now, we are going to setup AWS S3. First, we need to login to the AWS console. After successful login, we need to go to the S3 menu and create a new bucket as directed in the screenshot below:

Then, a window will open up where we need to enter the bucket name and choose the server region as directed in the screenshot below:

Initially, the bucket will be set to private. So, we need to make the bucket mode public by clicking on the Bucket name option:

Then, we need to select the Permissions tab as displayed in the code snippet below:

In the Permissions tab, we need to turn-off Block public access option:
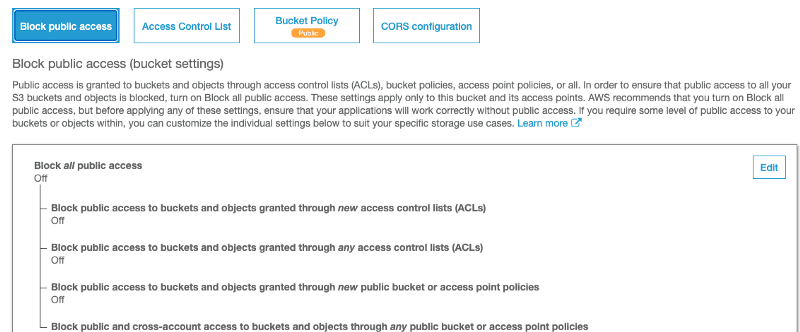
Now, we move on to the local deployment setup.
Step 3: Local Deployment
In this step, we are going to upload our react project directly from the local repository to S3 for testing purposes. Firstly, we need to go to My Security Credential as directed in the menu screenshot below:

Then, we need to create a new Access Key and download the key file by pressing the Download Key File button as shown in the screenshot below:

Next, we need to move back to our local repo of our project and install AWS CLI with Homebrew by running the following command in our project directory:
$ brew install awscli
Then, we need to run aws configure command and set AWS Access Key ID and AWS Secret Access Key as directed in the code snippet below:
$ aws configure
AWS Access Key ID [None]: xxxxxxxxxxx
AWS Secret Access Key [None]: xxxxxxxxxxx
Default region name [None]: ap-southeast-1
Default output format [None]: json
Now, we need to go back to the S3 project and navigate to Properties -> Static Web Hosting as directed in the screenshot below:

In the Static website hosting option, we need to enable the hosting as shown in the screenshot below:

Now, we are going to try and build our react project in order to sync with the AWS S3 bucket. For that, we need to run the commands given in the following snippet in our react project terminal:
$ yarn build
$ aws s3 sync build/ s3://myawesomeapp.com --delete(aws s3 sync <% path build folder %> s3://<% bucket-name %>/)
Here, ( -- delete) means we delete the default project file in the bucket then sync the new project.
If the build operation runs successfully, we will get the following result in our browser window:

Hence, we are done with the local deployment of our project. This also completes our setup of AWS S3 in sync with our React Native project.
Now, we move on to set up CircleCI in our react project.
Step 4: CircleCI Setup
First, we need to create an account on CircleCI. We can do that using GitHub login, which simplifies the register and login process. Then, we will be redirected to https://circleci.com/dashboard. If not, we need to go to the same URL which is the CircleCI dashboard.
In the dashboard, we need to click on Add Project.
In the Projects screen, we need to choose the repository that we want to follow by clicking on Set Up Project as directed in the screenshot below:

Now, we can set up the configuration process either on CircleCI or on local projects as well:

For local setup, we need to copy and paste the above code to our config file as shown in the code snippet below:
version: 2.1
orbs:
aws-s3: circleci/[email protected]
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: circleci/node:12.9.1-browsers
working_directory: ~/repo
steps:
- checkout
- restore_cache:
keys:
- v1-dependencies-{{ checksum "package.json" }}
# fallback to using the latest cache if no exact match is found
- v1-dependencies-
- run: yarn install
- save_cache:
paths:
- node_modules
- ~/.npm
- ~/.cache
key: v1-dependencies-{{ checksum "package.json" }}
- run: yarn lint
- run: yarn size
- run: yarn test
- run: yarn build
- aws-s3/sync:
from: build
to: "s3://kriss-react-cicd/"
arguments: |
--acl public-read \
--cache-control "max-age=86400"
overwrite: true
For CircleCI, we need to go to the CircleCI dashboard and create a new branch and initialize a ‘pull request’ for that new branch to the master branch. Then, we can work on that branch until deployment is successful as shown in the screenshot below:

Step 5: Setting up Environment Variables
Next, we are going to set up AWS credentials in CircleCI. Firstly, we need to click on the project:

Then inside the project dashboard, we need to click on Project Settings:

Inside the Project Settings option, we need to click on the Add Environment Variable button:

Then, we need to add the correct variables or correct the existing variables:

Now we have successfully configured the environment variables.
Step 6: Setting up AWS CloudFront
We know that we have already successfully deployed our React Native project to AWS from what we did before. However, it doesn't set up HTTPS, which makes the deployment insecure. In order to make the hosting secure, we can use AWS CloudFront.
In CloudFront, we need to go to the console and select Create Distribution -> Get Started. Then, we need to hit the Create Distribution button as directed in the screenshot below:

Next, we need to copy and paste the link from AWS S3 to the Origin Domain Name field as directed in the screenshot below:

In the Distribution options, we need to supply the following configurations:
Origin Domain Name: http://kriss-react-cicd.s3-website-ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/ (S3 endpoint )
Origin ID: kriss-react-cicd
Viewer Protocol Policy: Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
With a successful configuration, we will see the status In Progress. Then, after waiting for around 15 to 20 minutes, the status will change to Deployed:

After the status changes to Deployed, we will be able to access the site from the domain name https://dhhqbyhy7gv01.cloudfront.net/. Here, our transmission protocol is already set to HTTPS. The access site from the above domain name is shown in the demo screenshot below:

Hence, we have successfully set up the CircleCI and AWS CloudFront to our React Native project.
Conclusion
CircleCI can do more than what we learned in the article, and it is worth exploring further. It is highly advantageous to setup CI/CD when starting a new project. Running the test, build, and deployment manually can be hefty work and come at an unacceptable cost. CI/CD helps automate tasks to streamline workflows. The CI/CD process also helps identify bugs in the project more easily. Additional CI/CD options are available with alternatives such as Jenkins, Travis CI, etc.
Note that if you find any errors while following this article, do not hesitate to notify me. :)
References

